The historical land of Persia in southwest Asia is connected to the current country of Iran. The term Persia has been in use for many years and comes from an area of southern Iran once known as Persis, also known as Pārs or Parsa, and currently known as Fārs. We shall discuss Persia location in this section and how the contemporary term Iran replaced it over time. A few of Iran’s key traits will also be briefly discussed.
Ancient Persia, an introduction
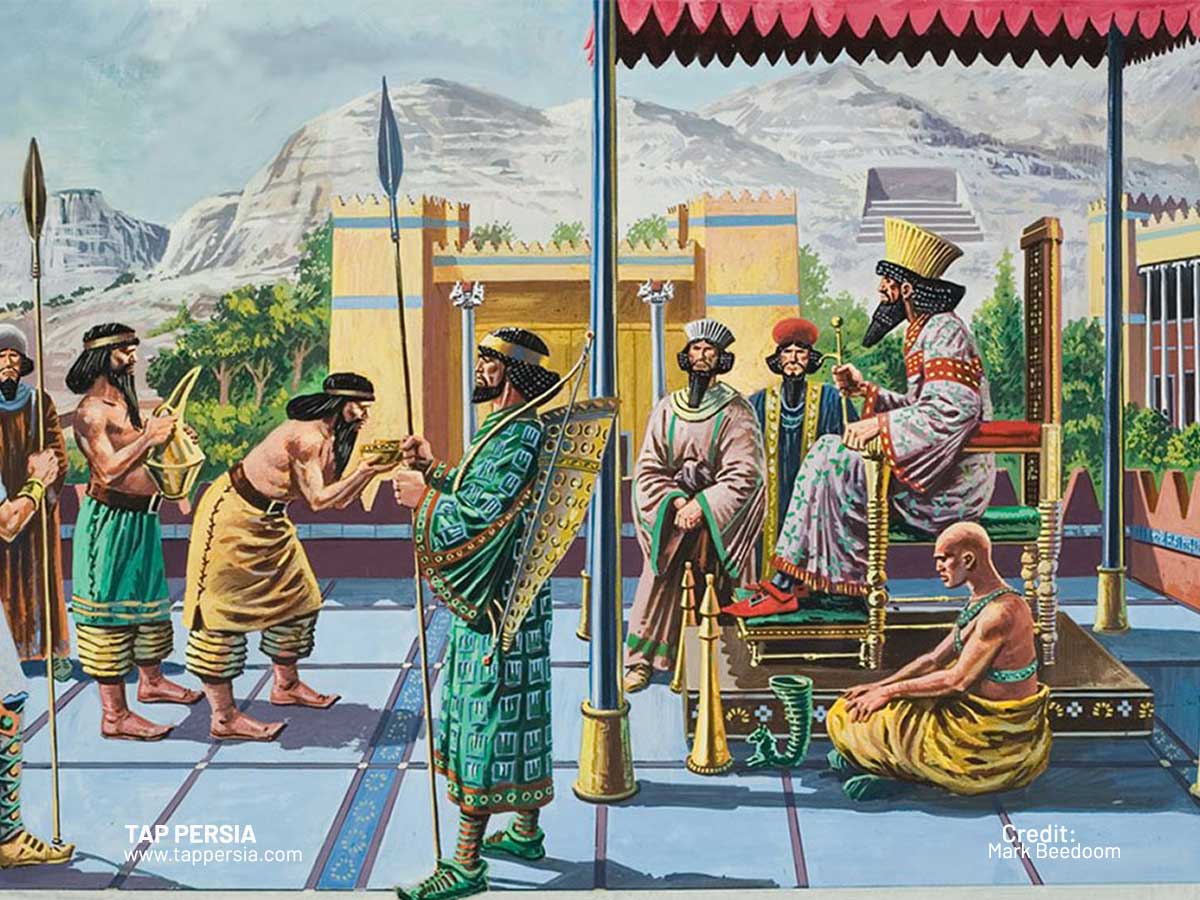

From the sixth century BC until the twentieth century AD, a number of dynasties made up the Persian Empire. The empire’s greatest extent was from the Indian Indus Valley to the Balkan Peninsula in Europe and south to Egypt. The Persian Empire was controlled by five dynasties before it fell in 1925. The empire’s borders fluctuated over the years, but Iran as it is today remained the economic and political hub of the empire.
Is Iran Persia?
The same country is commonly referred to by the names Iran and Persia. Iran today was the the ancient kingdom of Persia’s location. Because of the ancient Greek authors, the term “Persia” has become widely used in the west to refer to contemporary Iran. The word “Persia” was taken from “Pers” which is a western counterpart of “Pars”. The ancient Persian Empire’s capital was located in the Iranian region of Pars.
The Rise Of The Persian Empire
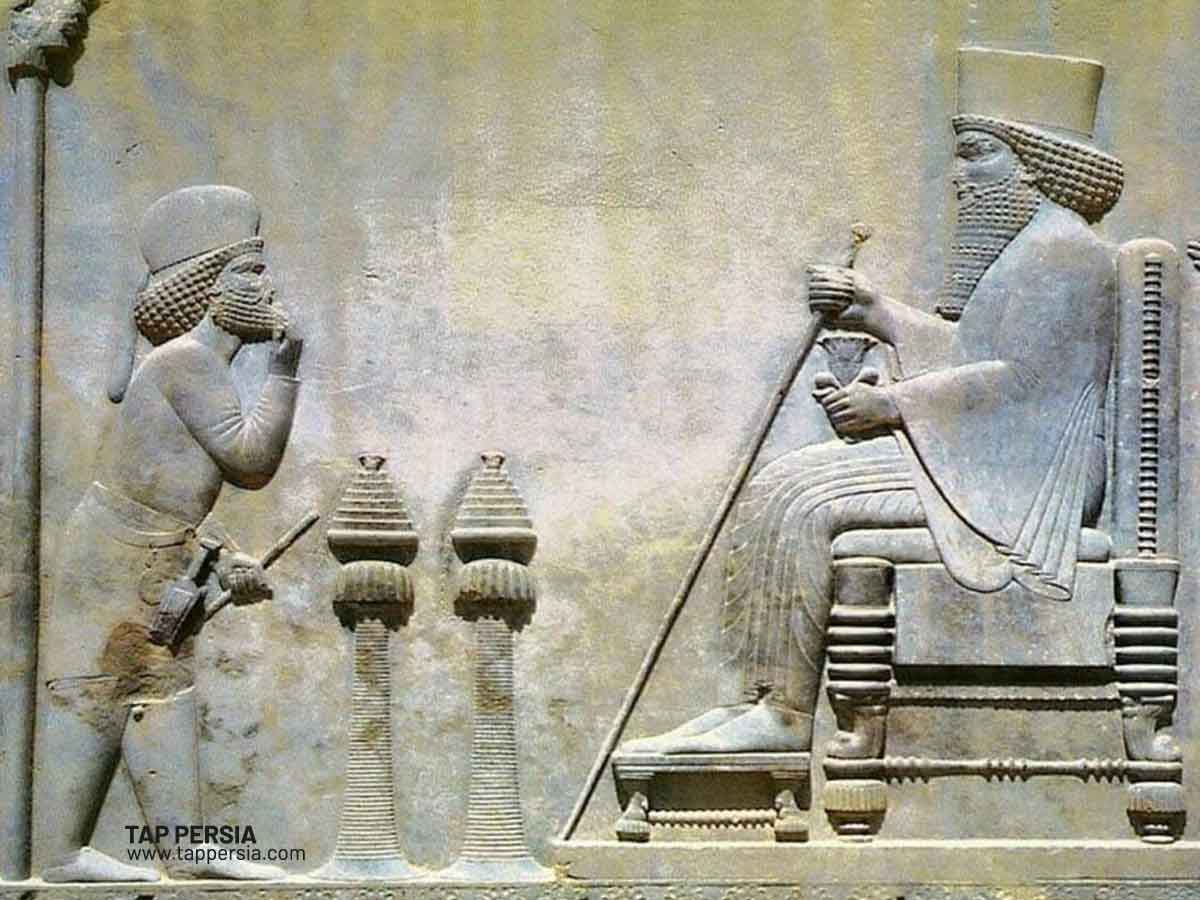

As King Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid ruled over the Aryan Kingdom in the sixth century, the Persian Empire was founded about the year 550 BCE. The ruler founded the Achaemenid Persian Empire by fusing the Aryan empires. By capturing non-Aryan lands, particularly those west of Persia, the king hoped to enlarge his realm. The empire reached as far east as the Indus Valley, as far west as Greece, and as far south as Egypt and Ethiopia. The empire grew fast and at one point surpassed all others in size.
Alexander of Macedonia seized control of the region in 330 BCE and founded the Seleucid Empire. The Parthian Empire was founded by the Aryan Parthians in 248 BCE after they conquered the Seleucids. Prior to the Persians’ second invasion and establishment of the Sasanian Empire in 226 CE, the Parthians held power. By founding the Safavid and Afsharid dynasties at the beginning of the sixteenth century, the Arabs took over the leadership of the empire.
First Use Of The Name Iran
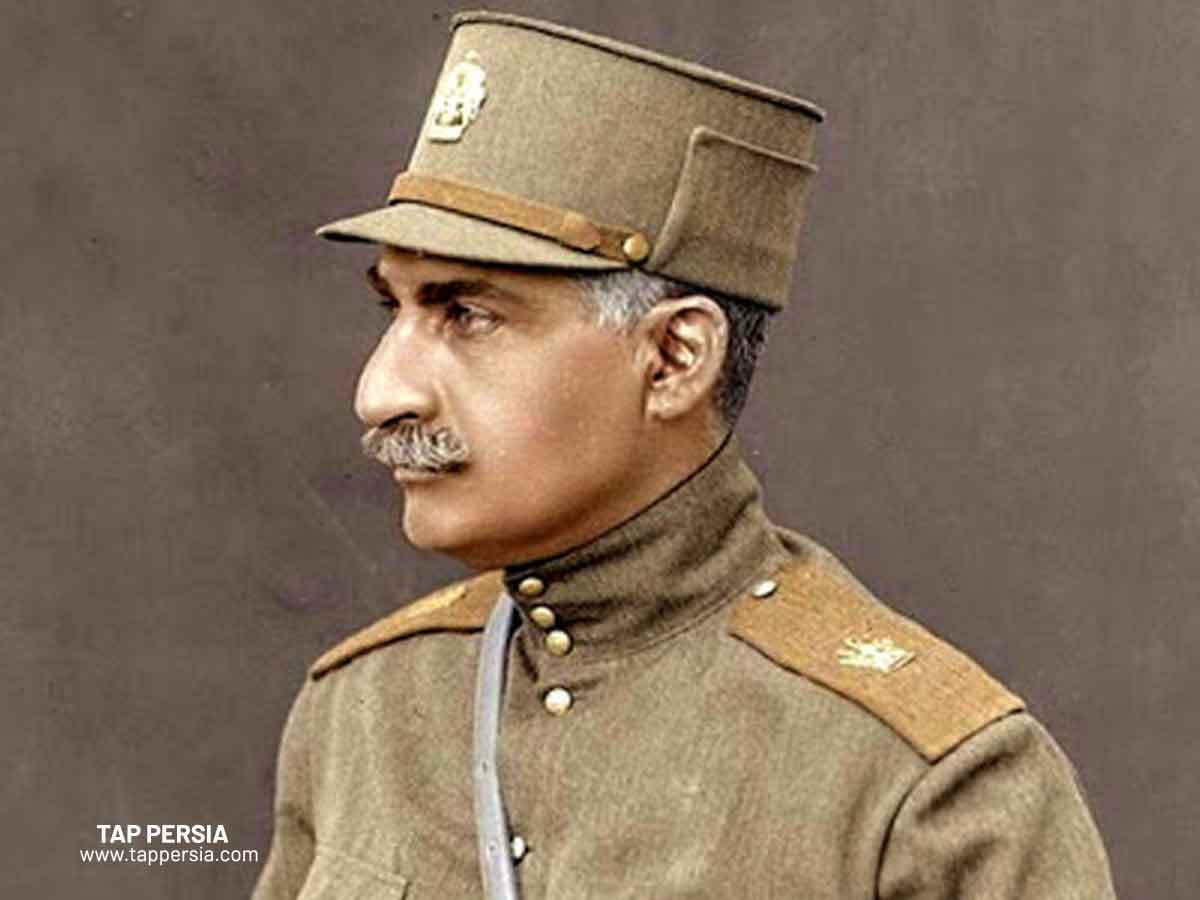

You might be wondering, when did Persia become Iran? The word “Iran” is derived from the word “Aryan,” which was the name of the first empire existing before the Persian Empire. The spread of the Aryan language, religion, and culture throughout the empire during the Persian era served as a unifying force.
Iran has never referred to its people as Persians or its nation as Persia. The west popularized this word’s usage. The then-ruler of Iran, Reza Shah Pahlavi, wanted to formally establish the usage of the term Iran in the West.
As a result, he issued a global circular asking foreign diplomatic missions in the nation to refer to the state as Iran and not Persia. The nation was officially acknowledged as Iran on March 21, 1935.
Geography
Iran, formerly known as Persia, is situated where South Asia, Central Asia, and the Arab states of the Middle East converge. Its name is pronounced “ee-raan”. Because of its strategic location and southern access to the Persian Gulf, Iran has always been a significant nation.
Because of its stunning but rather isolating geography, most of Iran is walled off from the outside world. Iran’s neighbors in the west are separated from it by high, rocky mountains, and the eastern part of the country is covered in a desolate, salty desert.
Lowlands surround the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman in Iran’s south, while a thin, fertile region abuts the Caspian Sea in the north. The majority of Iranians reside near the margins of a high plateau that runs across the center of the nation.
People & Culture

For thousands of years, Iranians have lived with strong religious convictions. Most Iranians identify as Muslims or as followers of Islam. In daily life, religion is essential.
Iranian scholarship has a lengthy history and has contributed to the country’s rich culture of music, food, literature, art, and architecture. Iranian philosophers and physicians from antiquity produced important works on philosophy and medicine, while an Iranian mathematician is credited with creating algebra. The universities of Iran are some of the best known in the region.
Nature
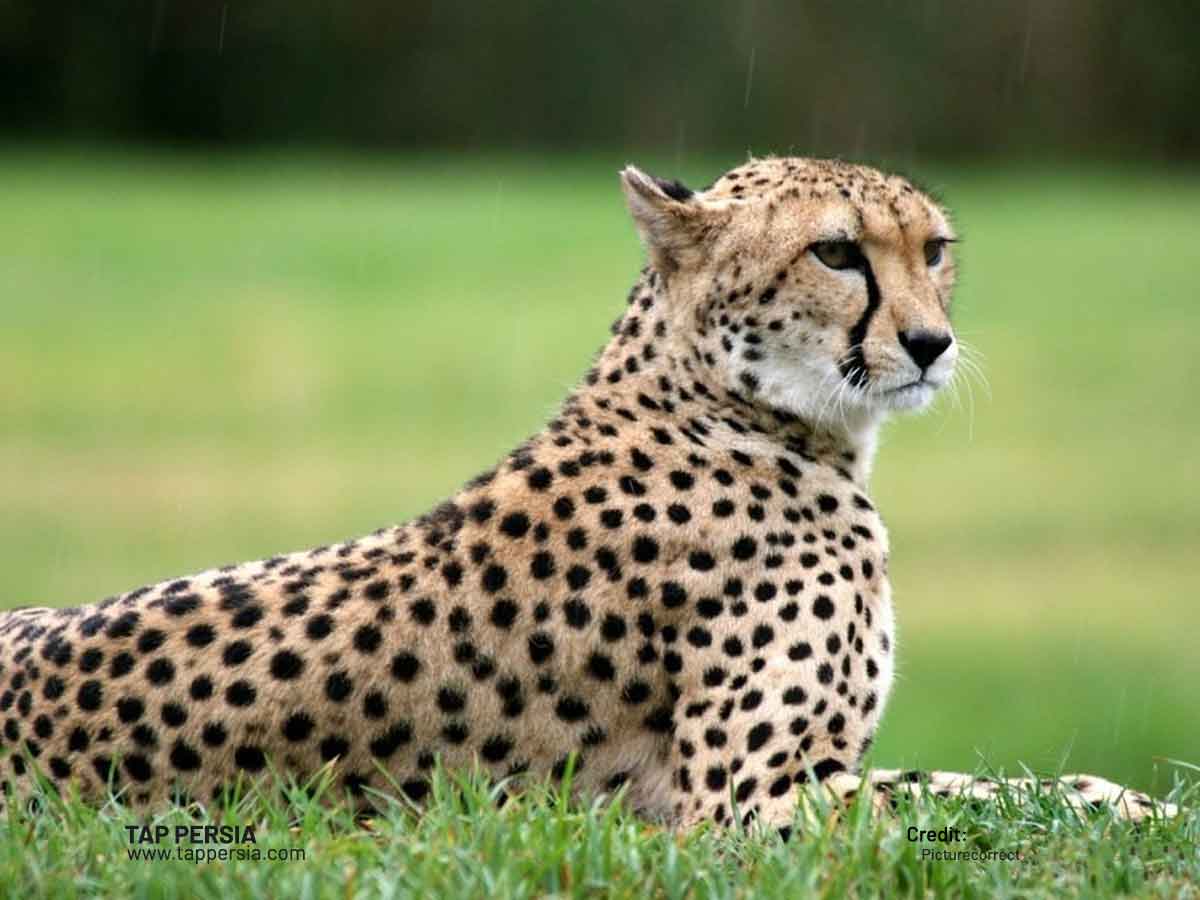

Iran had had a large population of tigers, lions, and other big animals. Regrettably, some species of these svelte hunters have become extinct, and they are now quite rare. Persian leopards and Asiatic cheetahs are both critically endangered. There are several parks and reserves in Iran where wildlife abounds. One of them, Kavir National Park, lies in the north-central area and is referred to as “Little Africa” since the vegetation and animals there are similar to those found in that continent. The only cheetahs in Iran may be found in this park.
Brown bears, leopards, wolves and wild goats may all be found in the highlands of Iran’s north and west, which are covered in lush woods. Animals including gazelles, hyenas, deer and jackals may be found on the country’s central plateau.
Government & Economy

The supreme leader, who is chosen by an organization of Islamic clerics known as the Assembly of Experts, is the figurehead of Iran’s administration. Second in command is a president who has been chosen by the people.
Despite having large oil reserves, Iran’s economy has been severely hampered since the United States implemented a trade embargo following the overthrow of the shah in 1979. Iran has been more isolated in recent years due to claims that it supports terrorism and suspicions that it is working on obtaining nuclear weapons.
What country is Persia now?
Iran is the modern-day equivalent of ancient Persia.
What countries made up Persia?
The Persian Empire, which is normally called the Achaemenid Empire, flourished from around 559 BCE to 331 BCE and was the biggest empire in history. At its height, it included parts of what are now Turkey, Afghanistan, Pakistan, Egypt, and Iran.
When did Iran become Persia?
The region presently known as Iran was known for the majority of history as Persia. It wasn’t until 1935 that it got its present name.
Why is Iran called Persia?
As Iran was created on the site of the ancient Persian Empire’s capital and the bulk of its first residents lived there, “Persia” is typically used to refer to Iran today. There are several diverse ethnic and tribal groupings in contemporary Iran.
Is Persia The old Iran?
Ancient Iran, commonly referred to as Persia, controlled western Asia for more than 12 centuries. Three consecutive indigenous dynasties—the Achaemenid, the Parthian, and the Sasanian—were in charge of an empire of unheard-of size and complexity.
How old is Iran?
Iran is one of the world’s oldest nations, with a history that dates back tens of thousands of years. In 3200 B.C., Susa, the first significant metropolis of the nation, was constructed on the central plateau. The Persian Empire formed in southwest Iran around 559 B.C. and subjugated the Egyptians and Mesopotamians.



Comment (0)